A Guide to bio-based and Biodegradable Packaging
What does what plastic is made from have to do with its effect on the environment? Does ‘plant-based’ mean the plastic will biodegrade the same way plants do? Do plant-based plastics have limited capabilities? Are plant-based plastics the same as bioplastics? And are they food-safe?
Here’s everything you need to know:
What are plant-based (or bio-based) plastics made of?
Plants! It might seem impossible when you see some of the incredible materials made entirely or partially from plant-based plastics, but plant-based plastics are plastics derived from plant material like corn, starch, seaweed, sugarcane, tree-pulp, bamboo fiber, and more.
Plant-based or bio-based plastics can be created using agricultural waste or scraps and reduce our dependence on petroleum, which currently requires about 8% of the world’s oil resources.
What’s the difference between plant-based (bio-based) plastic and bioplastic?
‘Plant-based’ and ‘bio-based’ are similar terms that refer to the source of the plastic polymers, while ‘bioplastic’ can refer to plastics whose feedstock is fully or partially sourced from biomass, biodegradable plastics, or plastics that are both bio-sourced and biodegradable. (https://bioplasticseurope.eu/about)
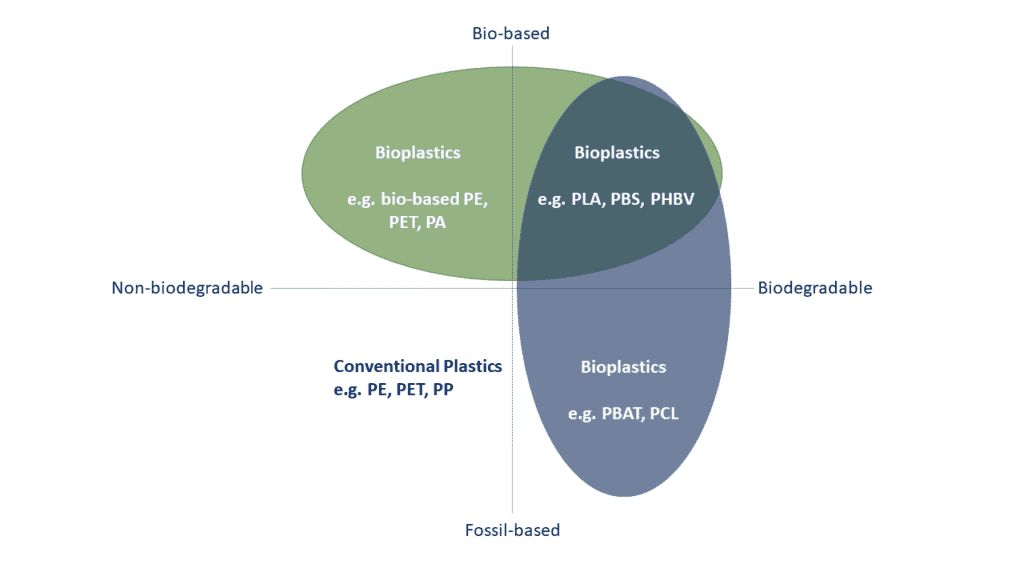
Is all plant-based plastic biodegradable?
No, Biodegradability doesn’t have to do with the source, but the chemical properties of the plastic. All plastics are made up of polymers (chains of molecules), built from monomers (single molecules), and these molecules can be derived from plant-based or petroleum-based sources.
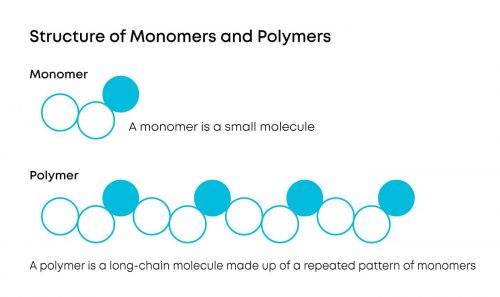
For a plastic to be biodegradable (or more specifically, compostable) the material needs to be able to disintegrate into smaller pieces and be ingested by microorganisms. This isn’t true of every plant-based plastic, but it is true of many.
If you are looking to purchase a bioplastic that will safely biodegrade, it’s important to check the disposal instructions on your plant based and bio-based plastics. Only certified compostable materials are tested to biodegrade under home and/or industrial compost conditions.
Are plant-based plastics better than conventional plastics?
What differentiates plant-based plastics from conventional plastics are what the material is sourced from. Plant-based plastics are plastics made from plant-derived molecules, as opposed to petroleum-derived molecules. In terms of their end-of-life, plant-based and petroleum-based plastics are the same (some will biodegrade in compost, while others will not). However, plant-based plastics are made from renewable materials, while petroleum-based plastics are made from a finite source of crude oil using energy-intensive processes to extract.
Are plant-based plastics good for the environment?
Plant-based plastics offer an alternative to fossil-based plastics, with a lot of the same capabilities. Sourcing from renewable plant-based materials instead of a finite source of petroleum is great for the environment and helps slow climate-change.
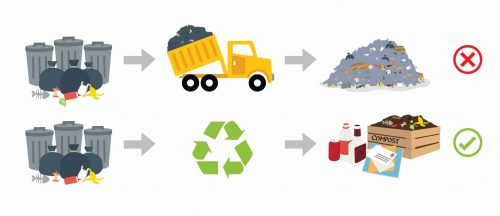
Do plant-based plastics reduce plastic pollution?

When looking for a plastic package that will not create harmful plastic waste, look for certified compostable plastics, which are tested to safely biodegrade under compost conditions.
Are all compostable plastics made from plant-based sources?
Although these eco-friendly polymers offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, their overall impact on the environment depends on production methods, disposal options, and end-of-life scenarios.
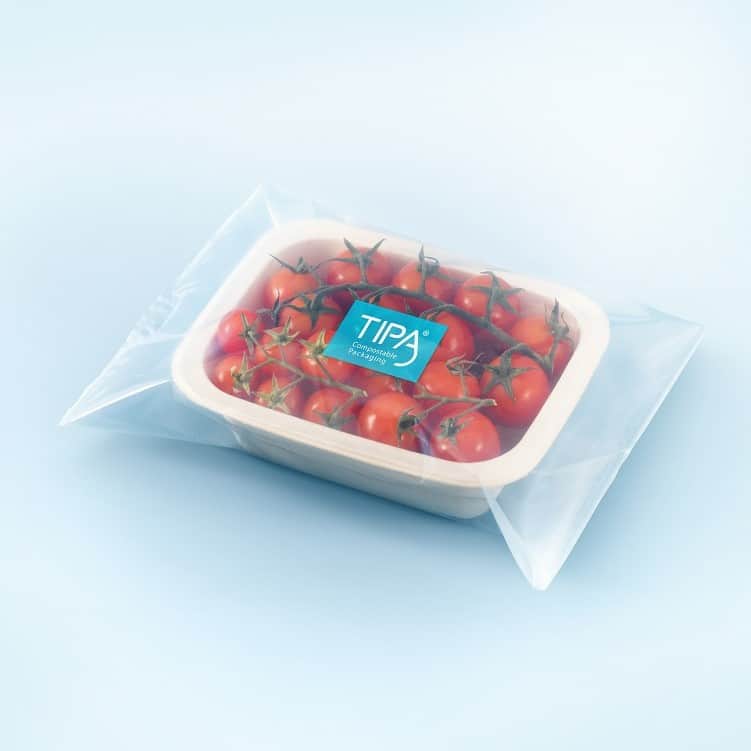
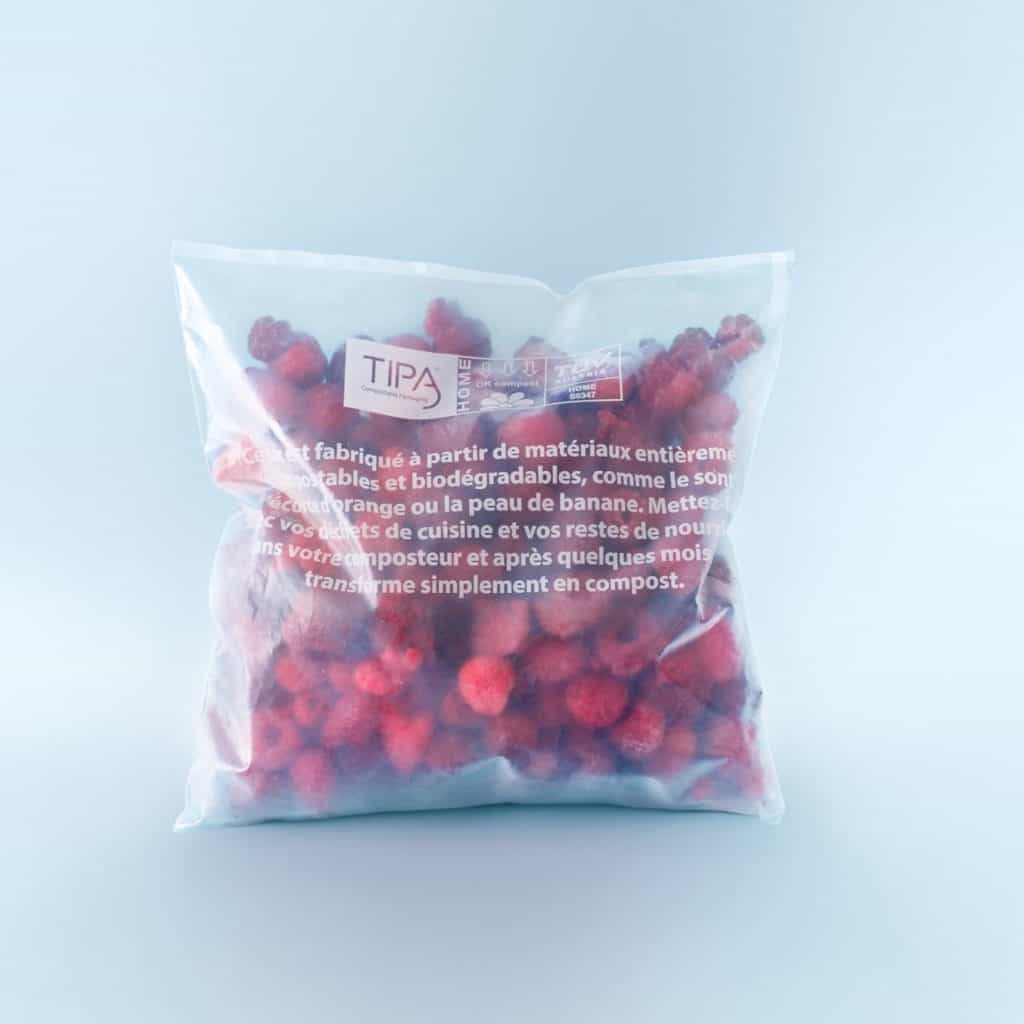
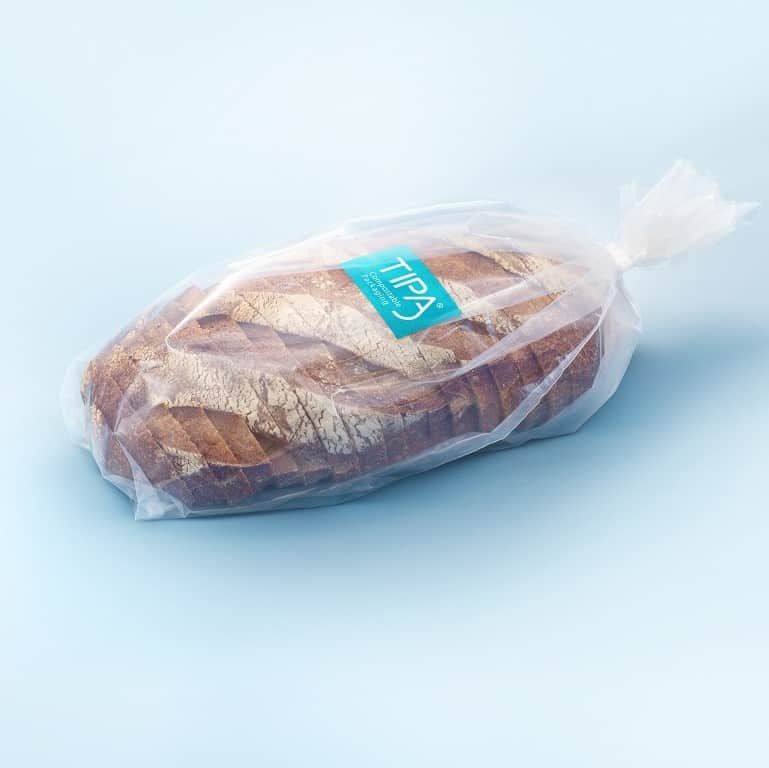
What makes a plastic compostable is how quickly and under what conditions the plastic will safely degrade under. Many compostable plastics (like TIPA’s!) are made from fossil and plant-based sources. TIPA’s packaging is certified to fully and safely compost according to international regulations in Australia, Europe, America, and Ireland.
What are plant-based plastics used for?
Plant-based plastics (or bioplastics) are used to create a lot of the same things that conventional petroleum-based plastics are used to create.
One popular use of plant-based plastics is in packaging, especially sustainable packaging and single-use plastics like food service wear (deli containers, cutlery, cups, and plastic bottles), laminated paper-trays, and compostable flexible packaging.
TIPA’s plant based packaging solutions are compostable, are food-safe and can be used for fresh produce, dry food, frozen food and more!


















